Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyato, Naoaki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J.*
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.821 - 824, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Zonal flow behaviour and its effect on turbulent transport in reversed shear tokamaks are investigated by global nonlinear simulation of ion temperature gradient driven turbulence. When safety factor  is reduced, zonal flows in a minimum
is reduced, zonal flows in a minimum  region change from oscillatory ones to stationary ones and suppress the turbulent transport effectively. This result indicates that the change of zonal flow behaviour in the minimum
region change from oscillatory ones to stationary ones and suppress the turbulent transport effectively. This result indicates that the change of zonal flow behaviour in the minimum  region may trigger the formation of ion transport barriers.
region may trigger the formation of ion transport barriers.
Ido, Takeshi*; Miura, Yukitoshi; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Kamiya, Kensaku; Hamada, Yasuji*; Nishizawa, Akimitsu*; Kawasumi, Yoshiaki*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 46(5), p.512 - 520, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:86 Percentile:92.73(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The electrostatic fluctuation spectrum and the fluctuation-induced particle flux of the JFT-2M tokamak were estimated using the hevy ion beam probe (HIBP) measurement. A geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) of the frequency about15kHz was identified in the L-mode. The GAM has its peak at about 3cm inside of the separatrix with the electric field of about 1.4kV/m. The estimated turbulent particle flux is found to be intermittent. It is found that the density fluctuation is modulated by the GAM in the wide frequency range and the coherence analysis shows that the flucruation-induced particle flux is partially contributed by the GAM. In the H-mode the GAM disappears and the fluctuation and the flux is much decreased.The mechanism of the large burst-like flux in the L-mode is not understood yet and left as the future problem.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Koide, Yoshihiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A55 - A61, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.933 - 941, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have investigated profile formation and sustainment of current hole (CH) plasma by 1.5D transport simulations with current limit model inside CH based on Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium. Sharp reduction of anomalous transport in RS region can reproduce JT-60U experiments. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in autonomous profile formation of ITB and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling. The scaling means that core plasma inside ITB is governed by MHD equilibrium limit, i.e., autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to penetration of inductive current. This shrink is prevented and CH size can be controlled by appropriate external CD. CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD. Application of CH plasma to reactor is discussed.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Profile formation and sustainment of tokamak plasmas with current hole (CH) have been investigated by using 1.5D transport simulations. A current limit model inside CH based on the Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium is introduced. We found that the sharp reduction of anomalous transport in the reversed-shear (RS) region can reproduce JT-60U experiment. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in the autonomous formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling, which means autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with the full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to inductive current penetration. This shrink is prevented and the CH size can be controlled by appropriate external current drive (CD). The CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD.
Connor, J. W.*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Garbet, X.*; Gormezano, C.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; ITB Database Group; ITPA Topical Group on Transport and Internal Barrier Physics*
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.R1 - R49, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:303 Percentile:76.74(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper first reviews the present state of theoretical and experimental knowledge regarding the formation and characteristics of ITBs in tokamaks. Specifically, the current status of theoretical modeling of ITBs is presented; then, an international ITB database based on experimental information extracted from some nine tokamaks is described and used to draw some general conclusions concerning the necessary conditions for ITBs to appear, comparing these with the theoretical models. The experimental situation regarding the steady-state, or at least quasi-steady-state, operation of tokamaks is reviewed and finally the issues and prospects for achieving such operational modes in ITER are discussed.

 plasmas
plasmasNeudatchin, S.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Shirai, Hiroshi; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Koide, Yoshihiko; Ito, Kimitaka*; Miura, Yukitoshi
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(12), p.1218 - 1220, 2003/12
New type of edge-core instantaneous interplay in JT-60U high-
 plasmas is found. Abrupt in time and wide in space reduction of electron heat flux in the core (called ITB-event) is correlated in ms timescale with the start of an ELM. This result gives a hint of the control to form the ITB immedeately and non-locally by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
plasmas is found. Abrupt in time and wide in space reduction of electron heat flux in the core (called ITB-event) is correlated in ms timescale with the start of an ELM. This result gives a hint of the control to form the ITB immedeately and non-locally by inducing the ELM-like MHD activity.
Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Li, J.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 79(5), p.478 - 488, 2003/05
This is a collection of review article related to the "Multiple Time and Spatial Scale Plasma Simulation" of various fields including fundamental research area of self-organization, magnetic and laser fusion field, space and astrophysics field where a plasma plays an essential roles.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2002-022, 149 Pages, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Takeji, Satoru; Isayama, Akihiko; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishii, Yasutomo; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Ishida, Shinichi; Kamada, Yutaka; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Yoshino, Ryuji; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology (JT-60 Special Issue), 42(2-3), p.278 - 297, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:6.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Naito, Osamu; Cui, Z.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Suzuki, Takahiro; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Seki, Masami; Hatae, Takaki; Fujita, Takaaki; Kondoh, Takashi; Shirai, Hiroshi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 89(6), p.065001_1 - 065001_4, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Evolution of lower hybrid (LH) driven current profile was measured during the formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) in a reversed magnetic shear discharge. As the ITB developed, initially centrally peaked LH driven current profile gradually turned hollow and was sometimes accompanied by an off-axis peak in electron temperature profile followed by a sawtooth-like instability localized to the ITB. These observations indicate the concentration of LH power deposition at the ITB and suggest the difficulty of current profile control by LH waves once the ITB is established.
Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Kitsunezaki, Akio; Shimizu, Masatsugu; Kuriyama, Masaaki; JT-60 Team; Kimura, Haruyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Sato, Masayasu; Isei, Nobuaki; et al.
Fusion Science and Technology, 42(1), p.7 - 31, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:27.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to establish scientific basis for the sustainment of highly integrated performance required in the advanced steady-state operation, JT-60U has been optimizing the discharge control scenarios of improved confinement plasmas and expanding the operation regions. Promising results toward the steady-state tokamak were obtained. The detail of such results is reported. JFT-2M has performed advanced and basic research for the development of high performance tokamak plasma as well as the structural material for a fusion reactor. The toroidal ripple reduction with ferritic steel plates outside the vacuum vessel was successfully demonstrated. No adverse effects were observed in the pre-testing on compatibility between ferritic steel plates, covering ~20% of the inside wall of the vacuum vessel, and plasma. The results of TRIAM-1M is also reported.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Shinohara, Koji
Review of Scientific Instruments, 73(3), p.1169 - 1176, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:68.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Australia Workshop on Plasma Diagnostics (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2002/00
The main purpose of JT-60U project is to make contribution to establishment of scientific basis of ITER and the demo tokamak reactor. Our ultimate goal is to achieve and sustain high integrated performance, namely high beta, high confinement, high bootstrap current fraction, full non-inductive current drive and heat/particle control, in a reactor-relevant regime. Toward this goal, we have developed weak magnetic shear ("high 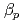 mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te
mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te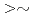 Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2000-035, 164 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Hatae, Takaki; Osborne, T. H.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Groebner, R. J.*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fukuda, Takeshi; Lao, L. L.*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 42(suppl.5A), p.A283 - A288, 2000/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:29.43(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Wakatani, Masahiro*; Fukuda, Takeshi; Toi, Kazuo*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Miura, Yukitoshi; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Oyabu, Nobuyoshi*; Hatae, Takaki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 76(2), p.175 - 177, 2000/02
no abstracts in English

 discharges in JT-60U
discharges in JT-60UKoide, Yoshihiko; Mori, Masahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Shirai, Hiroshi; Hatae, Takaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kimura, Haruyuki; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Isei, Nobuaki; Isayama, Akihiko; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 40(5), p.641 - 645, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:61.77(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
 p mode plasmas in the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute Tokamak-60 upgrade
p mode plasmas in the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute Tokamak-60 upgradeTakeji, Satoru; Kamada, Yutaka; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ishida, Shinichi; Takizuka, Tomonori; Neyatani, Yuzuru; Tokuda, Shinji
Physics of Plasmas, 4(12), p.4283 - 4291, 1997/12
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:50.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Yamagiwa, Mitsuru; *; M.Elia*
Physics of Plasmas, 4(11), p.4031 - 4034, 1997/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:8.87(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English